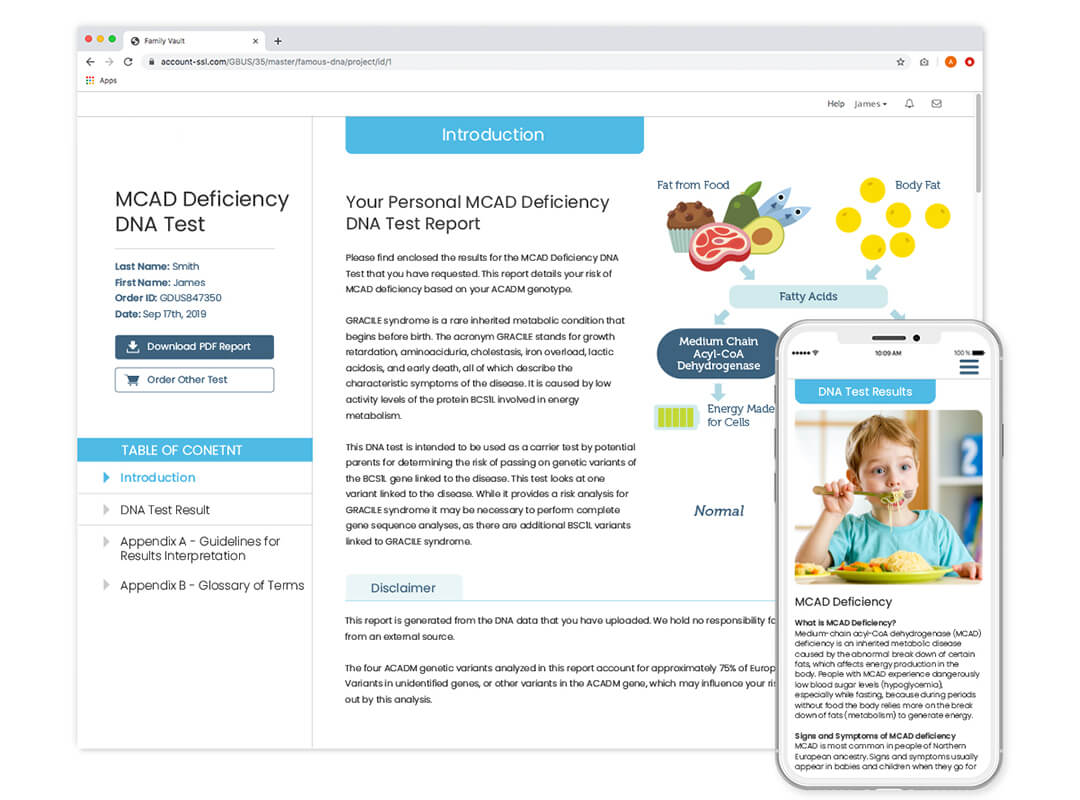
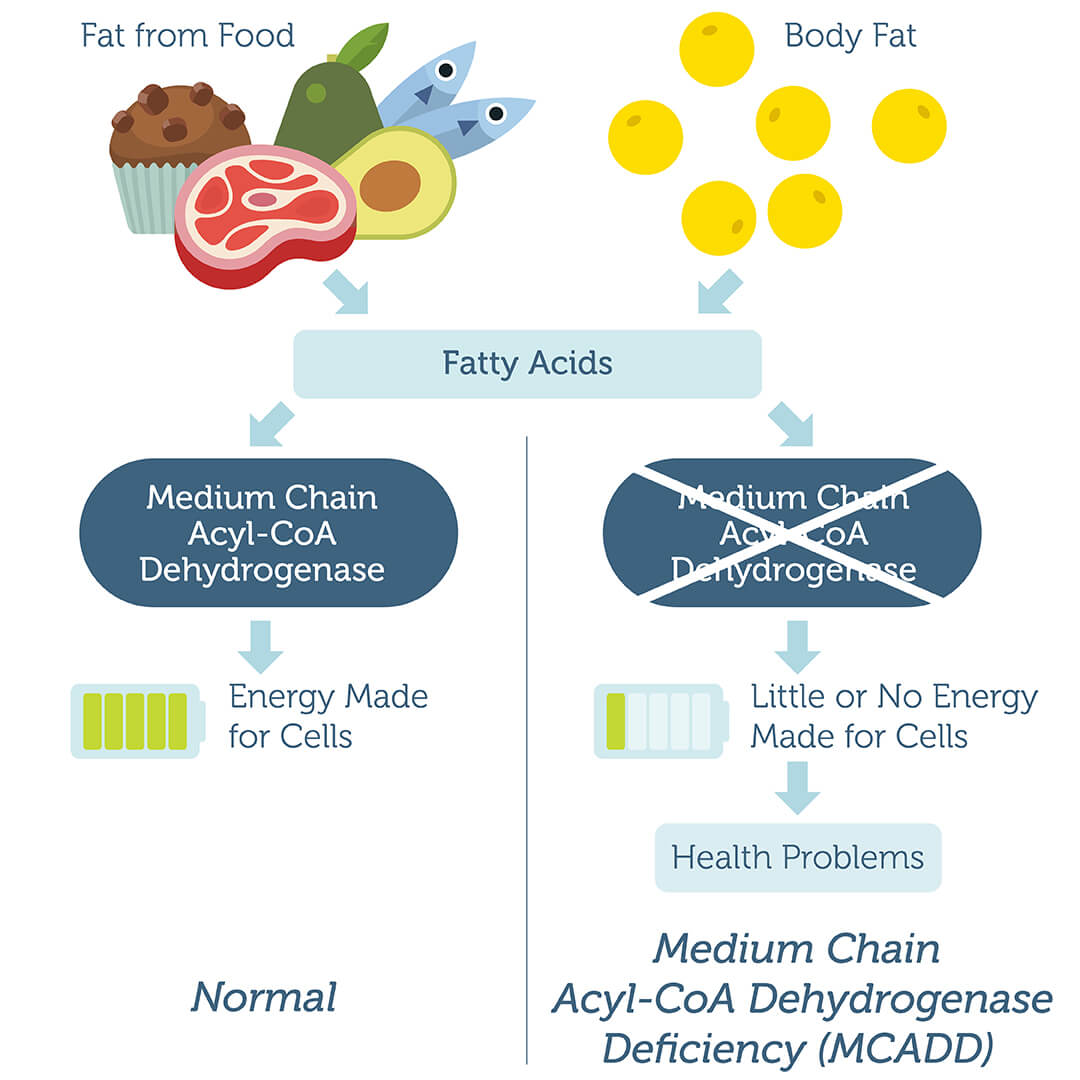
MCAD Deficiency DNA Test
Are you a genetic carrier for MCAD deficiency? Find out with this DNA Test.
- Detects four variants in the ACADM gene which cause MCAD deficiency
- Carrier screening test intended for couples who are planning to become pregnant
- Determine the risk of your child inheriting MCAD deficiency
- 100% private and confidential online results
Already have DNA markers? Sign in and upload your data to view results.
Need to take the DNA Test? Order our easy-to-use swab kit.