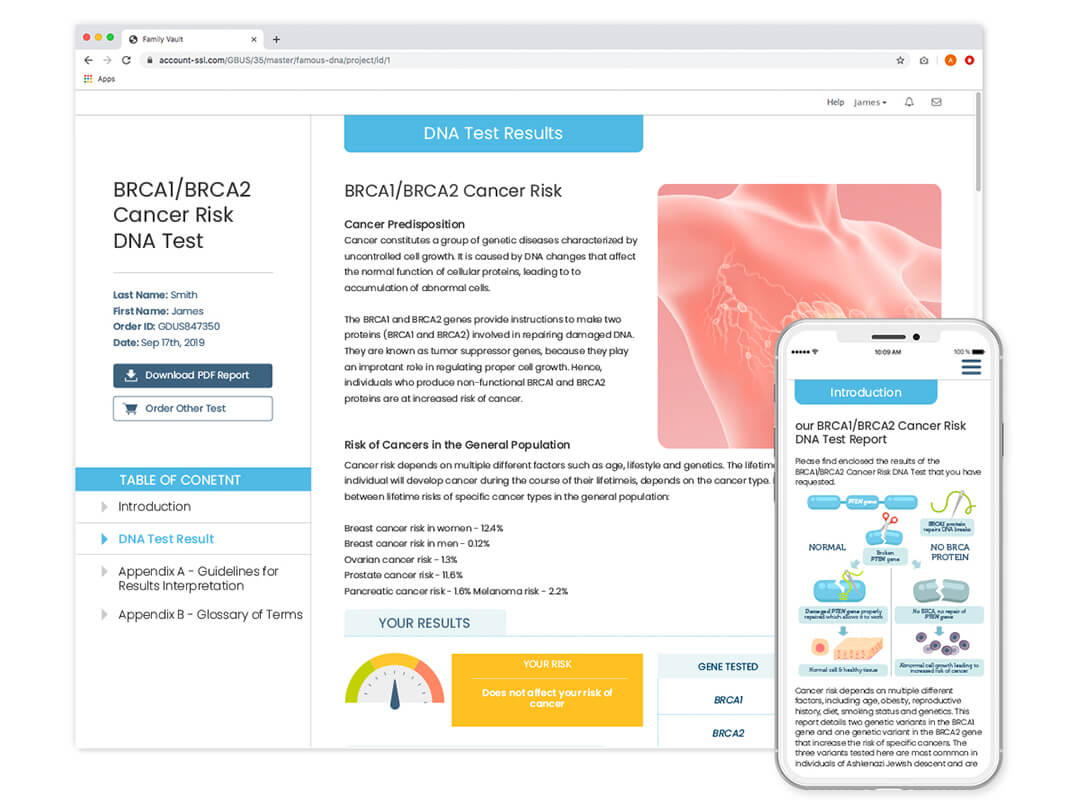
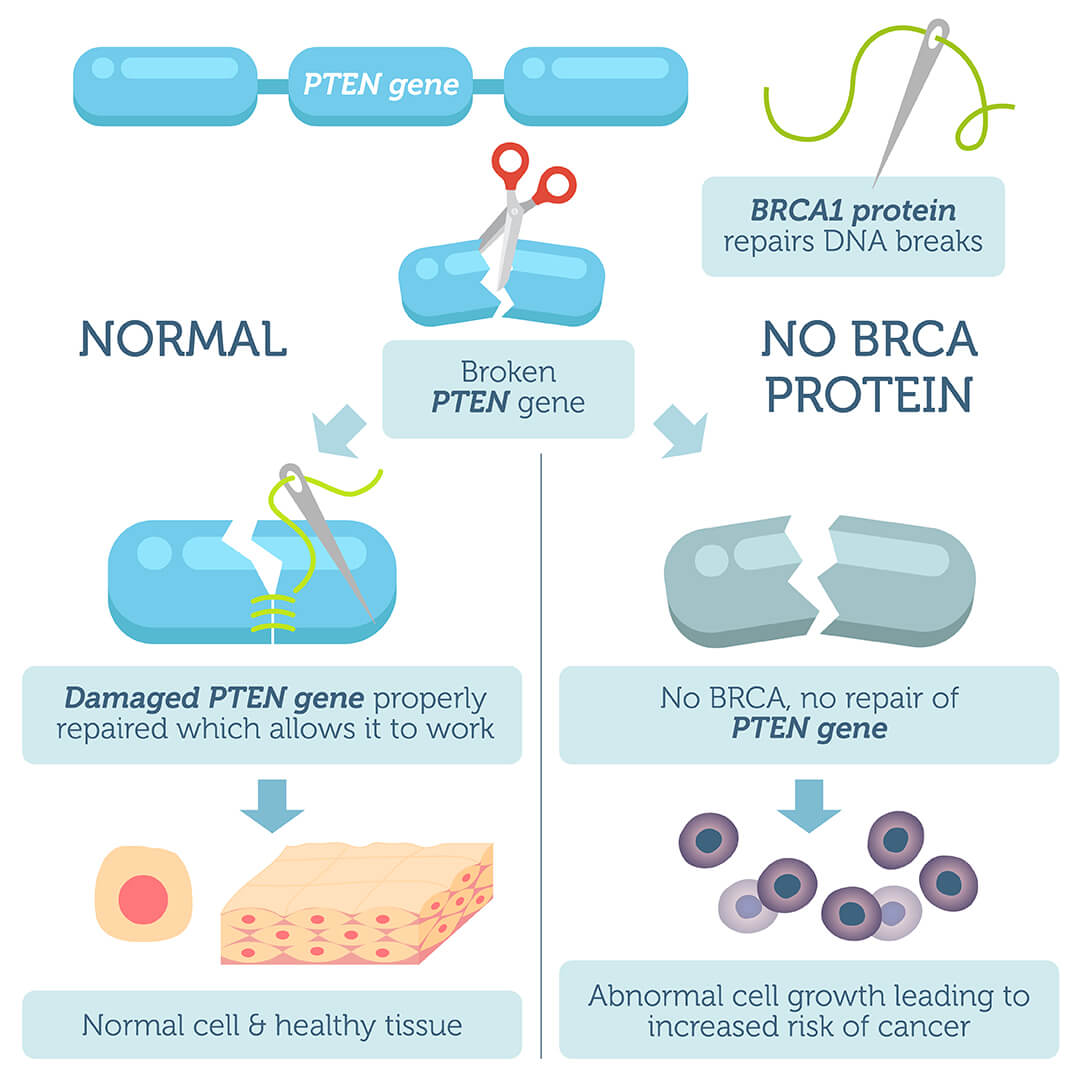
BRCA1/BRCA2 Cancer Risk DNA Test (Selected Variants Only)
Are you at increased risk of cancer? Find out with this DNA Test.
- Detects two BRCA1 variants and one BRCA2 variant linked to increased cancer risk
- These variants are most common in people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent
- 100% private and confidential online results
Already have DNA markers? Sign in and upload your data to view results.
Need to take the DNA Test? Order our easy-to-use swab kit.